- Block Data Access Of A App On Mac Free
- Mac App Data Location
- Block Data Access Of A App On Mac Download
Get apps from the Mac App Store. Reinstall apps from the Mac App Store. Manage cookies and other website data in Safari. Find a missing device. Mac hardware. Use trackpad and mouse gestures. Select the checkbox next to an app to allow it to access the microphone. Feb 22, 2019 How To Block Websites On Mac. Restricting access to apps and websites has been a feature on both Windows and Macs since the early days. Surprisingly, most people aren’t even aware this is a possibility or don’t use it as it seems to be too complicated to set up. We’ll start by tackling the flow for Parental Controls on Mac. Normally, H&R Block data files are located in the Documents folder, in a subfolder called HR Block. Available at participating offices and if your employer(s) participate in the W-2 Early Access SM program. Valid for 2017 personal income tax return only. Return must be filed January 5 - February 28, 2018 at participating offices to qualify.
-->This article lists and describes the different settings you can control on macOS devices. As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to allow or disable features, set password rules, allow or restrict specific apps, and more.
These settings are added to a device configuration profile in Intune, and then assigned or deployed to your macOS devices.
Note
The user interface may not match the enrollment types in this article. The information in this article is correct. The user interface is being updated in an upcoming release.
Before you begin
Create a macOS device restrictions configuration profile.
Note
These settings apply to different enrollment types. For more information on the different enrollment types, see macOS enrollment.
Built-in Apps
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Block Safari AutoFill: Yes disables the autofill feature in Safari on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to change autocomplete settings in the web browser.
Block use of camera: Yes prevents access to the camera on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow access to the device camera.
Intune only manages access to the device camera. It doesn't have access to pictures or videos.
Block Apple Music: Yes reverts the Music app to classic mode, and disables the Music service. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow using the Apple Music app.
Block spotlight suggestions: Yes stops Spotlight from returning any results from an Internet search. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Spotlight search to connect to the Internet, and get search results.
Block file transfer using Finder or iTunes: Yes disables application file sharing services. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow application file sharing services.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.13 and newer
Cloud and storage
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Block iCloud Keychain sync: Yes disables syncing credentials stored in the Keychain to iCloud. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to sync these credentials.
Block iCloud Desktop and Document Sync: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing documents and data. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow document and key-value synchronization to your iCloud storage space.
Block iCloud Mail Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing to the macOS Mail app. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Mail synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Contact Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing the device contacts. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow contact sync using iCloud.
Block iCloud Calendar Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing to the macOS Calendar app. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Calendar synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Reminder Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing to the macOS Reminders app. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Reminders synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Bookmark Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing the device Bookmarks. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Bookmark synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Notes Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing the device Notes. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Notes synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Photos backup: Yes disables iCloud Photo Library, and prevents iCloud from syncing the device photos. Any photos not fully downloaded from iCloud Photo Library are removed from local storage on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow syncing photos between the device and the iCloud Photo Library.
Block Handoff: This feature allows users to start work on a macOS device, and then continue the work they started on another iOS/iPadOS or macOS device. Yes prevents the Handoff feature on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow this feature on devices.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.15 and newer
Connected devices
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
- Block AirDrop: Yes prevents using AirDrop on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow using the AirDrop feature to exchange content with nearby devices.
- Block Apple Watch auto unlock: Yes prevents users from unlocking their macOS device with their Apple Watch. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to unlock their macOS device with their Apple Watch.
Domains
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
- Unmarked Email Domains: Enter one or more Email domain URLs to the list. When users send or receive an email from a domain other than the domains you added, the email is marked as untrusted in the macOS Mail app.
General
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Block Lookup: Yes prevents user from highlighting a word, and then looking up its definition on the device. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow the definition lookup feature.
Block dictation: Yes stops users from using voice input to enter text. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to use dictation input.
Block content caching: Yes prevents content caching. Content caching stores app data, web browser data, downloads, and more locally on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might enable content caching.
For more information on content caching on macOS, see Manage content caching on Mac (opens another website).
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.13 and newer
Defer software updates: Yes allows you to delay when software updates are shown on devices, from 0-90 days. This setting doesn't control when updates are or aren't installed. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might show updates on devices as Apple releases them. For example, if a macOS update gets released by Apple on a specific date, then that update naturally shows up on devices around the release date. Seed build updates are allowed without delay.
Delay visibility of software updates: Enter a value from 0-90 days. When the delay expires, users get a notification to update to the earliest version of the OS available when the delay was triggered.
For example, if a macOS update is available on January 1, and Delay visibility is set to 5 days, then the update isn't shown as an available update. On the sixth day following the release, that update is available, and users can install it.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.13.4 and newer
Block screenshots and screen recording: Device must be enrolled in Apple's Automated Device Enrollment (DEP). Yes prevents users from saving screenshots of the display. It also prevents the Classroom app from observing remote screens. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to capture screenshots, and allows the Classroom app to view remote screens.
Disable AirPlay, view screen by Classroom app, and screen sharing: Yes blocks AirPlay, and prevents screen sharing to other devices. It also prevents teachers from using the Classroom app to see their students' screens. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow teachers to see their students' screens.
To use this setting, set the Block screenshots and screen recording setting to Not configured (screenshots are allowed).
Allow Classroom app to perform AirPlay and view screen without prompting: Yes lets teachers see their students' screens without requiring students to agree. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might require students to agree before teachers can see the screens.
To use this setting, set the Block screenshots and screen recording setting to Not configured (screenshots are allowed).
Require teacher permission to leave Classroom app unmanaged classes: Yes forces students enrolled in an unmanaged Classroom course to get teacher approval to leave the course. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow students to leave the course whenever the student chooses.
Allow Classroom to lock the device without prompting: Yes lets teachers lock a student's device or app without the student's approval. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might require students agree before teachers can lock the device or app.
Students can automatically join Classroom class without prompting: Yes lets students join a class without prompting the teacher. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might require teacher approval to join a class.
Password
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Require password: Yes requires users to enter a password to access devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might not require a password. It also doesn't force any restrictions, such as blocking simple passwords or setting a minimum length.
Required password type: Enter the required password complexity level your organization requires. When left blank, Intune doesn't change or update this setting. Your options:
- Not configured: Uses the device default.
- Alphanumeric: Includes uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numeric characters.
- Numeric: Password must only be numbers, such as 123456789.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.10.3 and newer
Number of non-alphanumeric characters in password: Enter the number of complex characters required in the password, from 0-4. A complex character is a symbol, such as
?. When left blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.Minimum password length: Enter the minimum length the password must have, from 4-16 characters. When left blank, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block simple passwords: Yes prevents using simple passwords, such as
0000or1234. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow simple passwords.Maximum minutes of inactivity until screen locks: Enter the length of time devices must be idle before the screen is automatically locked. For example, enter
5to lock devices after 5 minutes of being idle. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.Maximum minutes after screen lock before password is required: Enter the length of time devices must be inactive before a password is required to unlock it. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Password expiration (days): Enter the number of days until the device password must be changed, from 1-65535. For example, enter
90to expire the password after 90 days. When the password expires, users are prompted to create a new password. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.Prevent reuse of previous passwords: Restrict users from creating previously used passwords. Enter the number of previously used passwords that can't be used, from 1-24. For example, enter 5 so users can't set a new password to their current password or any of their previous four passwords. When the value is blank, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block user from modifying passcode: Yes stops the passcode from being changed, added, or removed. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow passcodes to be added, changed, or removed.
Block Touch ID to unlock device: Yes prevents using fingerprints to unlock devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to unlock the device using a fingerprint.
Block password AutoFill: Yes prevents using the AutoFill Passwords feature on macOS. Choosing Yes also has the following impact:
- Users aren't prompted to use a saved password in Safari or in any apps.
- Automatic Strong Passwords are disabled, and strong passwords aren't suggested to users.
When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow these features.
Block password proximity requests: Yes prevents devices from requesting passwords from nearby devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow these password requests.
Block password sharing: Yes prevents sharing passwords between devices using AirDrop. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow passwords to be shared.
Privacy preferences
On macOS devices, apps and processes often prompt users to allow or deny access to device features, such as the camera, microphone, calendar, Documents folder, and more. These settings allow administrators to pre-approve or pre-deny access to these device features. When you configure these settings, you manage data access consent on behalf of your users. Your settings override their previous decisions.
The goal of these settings is to reduce the number of prompts by apps and processes.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.14 and newer
- Some settings apply to macOS 10.15 and newer.
- These settings only apply on devices that have the privacy preferences profile installed before being upgraded.
Settings apply to: User approved device enrollment, Automated device enrollment
- Apps and processes: Add apps or processes to configure access. Also enter:
Name: Enter a name for your app or process. For example, enter
Microsoft Remote DesktoporMicrosoft Office 365.Identifier type: Your options:
- Bundle ID: Select this option for apps.
- Path: Select this option for non-bundled binaries, which is a process or executable.
Helper tools embedded within an application bundle automatically inherit the permissions of their enclosing application bundle.
Identifier: Enter the app bundle ID, or the installation file path of the process or executable. For example, enter
com.contoso.appname.To get the app bundle ID, open the Terminal app, and run the
codesigncommand. This command identifies the code signature. So you can get the bundle ID and the code signature simultaneously.Code requirement: Enter the code signature for the application or process.
A code signature is created when an app or binary is signed by a developer certificate. To find the designation, run the
codesigncommand manually in the Terminal app:codesign --display -r - /path/to/app/binary. The code signature is everything that appears after=>.Enable static code validation: Choose Yes for the app or process to statically validate the code requirement. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Enable this setting only if the process invalidates its dynamic code signature. Otherwise, use Not configured.
Block Camera: Yes prevents the app from accessing the system camera. You can't allow access to the camera. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block Microphone: Yes prevents the app from accessing the system microphone. You can't allow access to the microphone. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block screen recording: Yes blocks the app from capturing the contents of the system display. You can't allow access to screen recording and screen capture. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Block input monitoring: Yes blocks the app from using CoreGraphics and HID APIs to listen to CGEvents and HID events from all processes. Yes also denies apps and processes from listening to and collecting data from input devices, such as a mouse, keyboard, or trackpad. You can't allow access to the CoreGraphics and HID APIs.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Speech recognition: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access the system speech recognition, and allows sending speech data to Apple.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing the system speech recognition, and prevents sending speech data to Apple.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Accessibility: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access to the system Accessibility app. This app includes closed captions, hover text, and voice control.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing the system Accessibility app.
Contacts: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access contact information managed by the system Contacts app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this contact information.
Calendar: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access calendar information managed by the system Calendar app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this calendar information.
Reminders: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access reminder information managed by the system Reminders app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this reminder information.
Photos: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access the pictures managed by the system Photos app in
~/Pictures/.photoslibrary. - Block: Prevents the app from accessing these pictures.
Media library: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access Apple Music, music and video activity, and the media library.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this media.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
File provider presence: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access the File Provider app, and know when users are using files managed by the File Provider. A File Provider app allows other File Provider apps to access the documents and directories stored and managed by the containing app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing the File Provider app.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Full disk access: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access all protected files, including system administration files. Apply this setting with caution.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these protected files.
System admin files: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access some files used in system administration.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Desktop folder: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files in the user’s Desktop folder.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Documents folder: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files in the user’s Documents folder.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Downloads folder: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files in the user’s Downloads folder.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Network volumes: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files on network volumes.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Removable volumes: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files on removable volumes, such as a hard disk.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
System events: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to use CoreGraphics APIs to send CGEvents to the system event stream.
- Block: Prevents the app from using CoreGraphics APIs to send CGEvents to the system event stream.
Apple events: This setting allows apps to send a restricted Apple event to another app or process. Select Add to add a receiving app or process. Enter the following information of the receiving app or process:
Identifier type: Select Bundle ID if the receiving identifier is an application. Select Path if the receiving identifier is a process or executable.
Identifier: Enter the app bundle ID, or the installation path of the process receiving an Apple event.
Code requirement: Enter the code signature for the receiving application or process.
A code signature is created when an app or binary is signed by a developer certificate. To find the designation, run the
codesigncommand manually in the Terminal app:codesign --display -r -/path/to/app/binary. The code signature is everything that appears after=>.Access: Allow a macOS Apple Event to be sent to the receiving app or process. Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app or process to send the restricted Apple event to the receiving app or process.
- Block: Prevents the app or process from sending a restricted Apple event to the receiving app or process.
Save your changes.
Restricted apps
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Type of restricted apps list: Create a list of apps that users aren't allowed to install or use. Your options:
- Not configured (default): Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, users might have access to apps you assign, and built-in apps.
- Approved apps: List the apps that users are allowed to install. To stay compliant, users must not install other apps. Apps that are managed by Intune are automatically allowed, including the Company Portal app. Users aren't prevented from installing an app that isn't on the approved list. But if they do, it's reported in Intune.
- Prohibited apps: List the apps (not managed by Intune) that users aren't allowed to install and run. Users aren't prevented from installing a prohibited app. If a user installs an app from this list, it's reported in Intune.
Apps list: Add apps to your list:
App Bundle ID: Enter the bundle ID of the app. You can add built-in apps and line-of-business apps. Apple's web site has a list of built-in Apple apps.
To find the URL of an app, open the iTunes App Store, and search for the app. For example, search for
Microsoft Remote DesktoporMicrosoft Word. Select the app, and copy the URL. You can also use iTunes to find the app, and then use the Copy Link task to get the app URL.App name: Enter a user-friendly name to help you identify the bundle ID. For example, enter
Intune Company Portal app.Publisher: Enter the publisher of the app.
Import a CSV file with details about the app, including the URL. Use the
<app bundle ID>, <app name>, <app publisher>format. Or, Export to create a list of apps you added, in the same format.
Next steps
Assign the profile and monitor its status.
You can also restrict device features and settings on iOS/iPadOS devices.
One-click website blocker
The web has the capacity to be both a blessing and a curse at the same time. On the one hand, it enables us to do the work we do and access the wealth of human knowledge. On the other hand, it distracts us from our goals and can even be outright dangerous for our kids.
Naturally, the topic of limiting web access has been in discussion for decades now. How do we block websites full of porn for our kids? What does blocking websites like Facebook and YouTube mean for a modern workplace? Why do we need to restrict ourselves with website blockers to resist temptation and distractions?
All these are valid questions we’ll explore below, in addition to showing you the best ways to block websites that seem to steal your attention all day long.
Get a solution for sites blocking
Install Setapp on Mac and boost your browsing experience. Or, rather let Setapp boost it by blocking sites that distract you.
How To Block Websites On Mac
Restricting access to apps and websites has been a feature on both Windows and Macs since the early days. Surprisingly, most people aren’t even aware this is a possibility or don’t use it as it seems to be too complicated to set up.
We’ll start by tackling the flow for Parental Controls on Mac. If you’ve used a similar feature on Windows before called Family Safety, the steps would sound familiar, although there are some key differences.
Blocking websites with Parental Controls
As the name suggests, the Parental Controls feature was developed by Apple to help parents put certain restrictions on their kids, such as accessing adult websites, addictive games, endless video streams, etc.
Lately, however, it hasn’t been uncommon for employers to set Parental Controls for their employees, mostly to limit social media usage or deter them from reading news websites throughout the day.
Regardless of your intended application for Parental Controls, here’s how to set it up:
- Open Parental Controls from System Preferences
- If you have an account you want to restrict already set up, just choose it from the list. If you don’t, click to create a new user account and then Continue.
- Fill out all the necessary information and click Create User
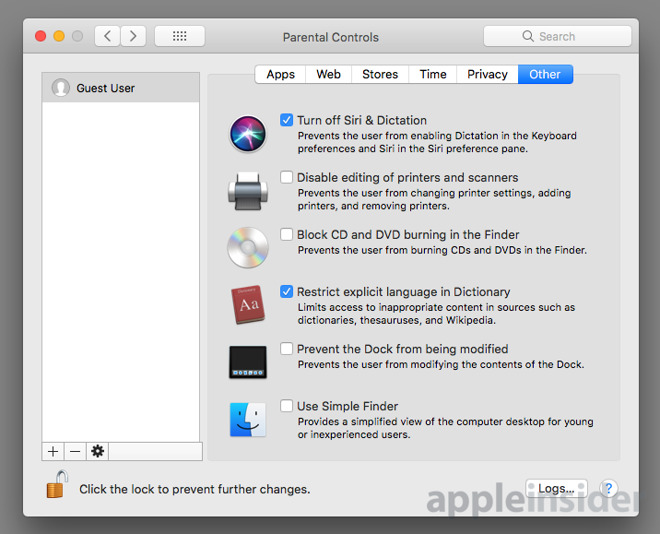
Now you should see the full Parental Controls menu with tabs such as Apps, Web, Stores, Time, Privacy, and Other. Feel free to explore all of them and set the restrictions that you deem a good fit. But first, let’s walk through the most popular setups.
To limit your kids exposure to adult websites, go over to the Web tab and choose “Try to limit access to adult websites.” Click Customize to enter websites you want your kids to visit at any time or never go to at all. Similarly, if you don’t want your employees wasting time on social media, you can include any those websites here too.
If you only allow children to visit a handful of websites overall, then choose “Allow access to only these websites” and list them all in the window below using the plus button.
To limit certain apps, navigate to the Apps tab and check “Limit Applications on this Mac.” Now in the Allowed Apps window, click on the dropdown arrow and select any applications that you’re fine with kids having access to.
When you are done, simply click the padlock icon on the bottom left to lock your settings in place. If you want to ensure that over time you kids don’t find a sneaky way to go around your settings, you can infrequently monitor their logs by going into the Logs menu available on the bottom right of your Parental Controls panel.
One important mention is that if you are searching for how to block a website on Chrome or how to block website on Safari, this description above is the way to do it. Parental Controls doesn’t differentiate between browsers, so its settings will work on Safari, Chrome, Firefox, or any other browser you use.
Easily block websites without changing settings
The truth is Parental Controls are somewhat complicated. It takes a while to get all the settings just right. And every time you catch your kids coming up with a new workaround, you have to devise a way to solve that too.
And what if you share the same computer with your children? Then you need to log out and log in every time you pass the laptop to each other. Some of us just don’t need those complications and wish there was an easier way. Luckily, there is.
Meet Focus - a simple website blocker that also works for apps and even specific webpages, all right from your Mac’s menu bar.
To block out distractions in Focus:
- Click on the app’s icon in the menu bar > Preferences
- Navigate to the Blocking tab
- Add any websites, webpages, and applications to the list using plus icons at the bottom. You’re done!
The beauty of Focus is that it doesn’t enforce the focus mode all the time - it works in sessions, which is perfect for sharing the same computer with your kids. So when your kids are asking for some playtime, you can just click on the app’s icon and select “Focus for 25 minutes” or “Custom focus...” to set the period of time during which blocking websites will be enforced.
To prevent your kids from changing settings, just go to Preferences again and, in the General tab, check the “Hardcore mode.” For extra safety, you can also turn on the “Password mode.”
What if your kids have their own computer? Not a problem. In the Preferences window, you can choose Schedule and set the limits you desire.
Eliminate distractions to be more productive
Another major advantage of Focus over Parental Controls is that it works not only for your kids but for you too. Don’t you sometimes wish you could block websites on Mac? Turn off YouTube, eliminate Facebook, stay away from Reddit - Focus makes it easy.
Just follow the same instructions as you would for your kid: block websites and apps, set up a schedule that mirrors your work hours, and lock preferences during sessions to minimize temptation.
As we all know, it’s impossible to work undistracted for eight hours straight. In fact, small breaks throughout the day are highly beneficial to your productivity. Focus allows you to turn off the website blocker for a small amount of time in the Break mode.
The app would also delight the followers of the Pomodoro technique, which automatically lets you have a short break after an intensive focus session. You can set it up your break periods in Preferences as well.
For extra motivation, you can include a list of your favorite “go get it” phrases in the Quotes tab in the app’s preferences as well. These quotes will appear when you try to access one of the blocked websites and remind you to get back to what’s truly important.
Block Data Access Of A App On Mac Free
Quickly concentrate on the task at hand
If Focus can easily solve all your problems related to blocking websites and apps that waste your time, it won’t really help you concentrate on a single task amidst your cluttered desktop and a heap of open windows. That’s where you need HazeOver.
Mac App Data Location
HazeOver is essentially a professional screen dimmer. While it’s not a way to block websites on Mac, it’s the perfect solution for your scattered focus. What this app does is highlighting the currently active window and dimming the rest of the screen, including notifications and other apps.
Even though HazeOver is simple in its application, it allows you to fine-tune every single setting to suit your needs. By going to its preferences from the menu bar icon, you can set how strong the dimming effect is, whitelist apps you don’t want dimmed, which is useful when you work with two windows at the same time, and configure how the apps will work on two or more displays.
As a bonus, HazeOver is perfect for working at night, as it only lets the light from the active app window to go through instead of overwhelming you with an ocean of blue light, which will make it harder to fall asleep later on. Similarly, watching a movie in the evening is so much more pleasant when HazeOver is there to dim everything around the video app.
Use the right website blocker at the right time
Overall, if you’ve used to tinker with all the complex settings in Family Safety on Windows or simply like the granular level of control, using Parental Controls is certainly an option.
For the rest of us, using Focus + HazeOver presents a much more flexible solution - one that can protect our kids and not let us slack off at the same time.
Block Data Access Of A App On Mac Download
A bundle of apps for free
Every app mentioned above is a part of Setapp. By downloading one, you get access to everything you need to improve browsing.
Best of all, both Focus and HazeOver are available on Setapp, a platform of over 150 highly acclaimed tools, utilities, and apps for your Mac. Sign up to become a Setapp member and try Focus, HazeOver, and all other apps from its catalogue for free during your trial period. In the meantime, how to block websites on Mac should no longer be a pressing issue.